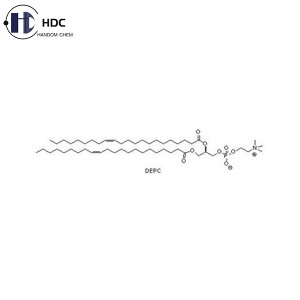
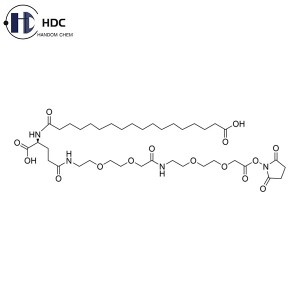
Soy Lecithin (Pharma Grade)
Brief Introduction to Phospholipids:
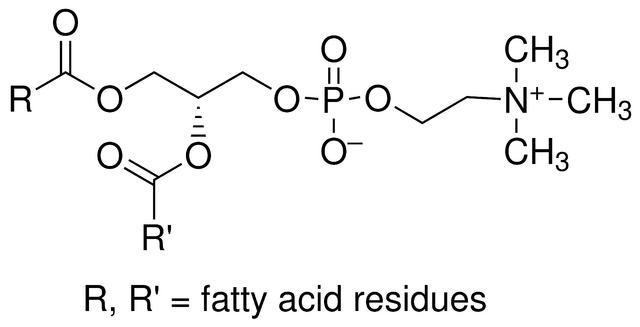
Phospholipids are a type of lipid containing phosphorus, including glycerophospholipids and sphingomyelin. Glycerophospholipids are widely distributed in animals, plants and microorganisms, while sphingomyelins are generally only distributed in animals and microorganisms, and are extremely rare in plants. Commodity phospholipids mostly refer to glycerophospholipids, such as plant phospholipids (soybean phospholipids, rapeseed phospholipids, cottonseed phospholipids, etc.) and egg yolk phospholipids, whose main components are phosphatidylcholine (PC), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), and phosphatidylinositol (PI).
The chemical name of lecithin is phosphatidylcholine (PC for short), according to its purity, it is generally divided into PC50, PC60, PC70, PC80, PC90, PC95 and other product forms. The highest purity can be purified to 98%, since the higher the purity, the stronger the oxidation performance, the lecithin purified to 98% needs to be hydrogenated before preservation. Lecithin that has not been hydrogenated is generally required to be stored in a sealed container filled with nitrogen.
Pure lecithin is a colorless, odorless, white solid at room temperature. In fact, it appears light yellow to brown due to different preparation or refining methods and storage conditions.
Ordinary Pharmaceutical Grade Soya Lecithin:
Ordinary pharmaceutical grade soybean lecithin (phosphatidylcholine, referred to as PC) is a yellow waxy product made from soybean powder lecithin as raw material, extracted through ethanol and other processes using original patented equipment (ZL2017.20049599.7; ZL2010.20147413.X). The main specifications include PC-50 and PC-70.
Product Specifications:
| Physical and Chemical Indicators | ||
| PC-50 | PC-70 | |
| Appearance | Yellow waxy solid | |
Brief Introduction to Phospholipids:
Phospholipids are a type of lipid containing phosphorus, including glycerophospholipids and sphingomyelin. Glycerophospholipids are widely distributed in animals, plants and microorganisms, while sphingomyelins are generally only distributed in animals and microorganisms, and are extremely rare in plants. Commodity phospholipids mostly refer to glycerophospholipids, such as plant phospholipids (soybean phospholipids, rapeseed phospholipids, cottonseed phospholipids, etc.) and egg yolk phospholipids, whose main components are phosphatidylcholine (PC), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), and phosphatidylinositol (PI).
The chemical name of lecithin is phosphatidylcholine (PC for short), according to its purity, it is generally divided into PC50, PC60, PC70, PC80, PC90, PC95 and other product forms. The highest purity can be purified to 98%, since the higher the purity, the stronger the oxidation performance, the lecithin purified to 98% needs to be hydrogenated before preservation. Lecithin that has not been hydrogenated is generally required to be stored in a sealed container filled with nitrogen.
Pure lecithin is a colorless, odorless, white solid at room temperature. In fact, it appears light yellow to brown due to different preparation or refining methods and storage conditions.