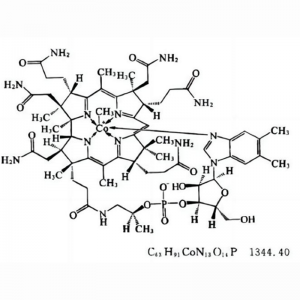
Mecobalamin
Chemical Structural Formula
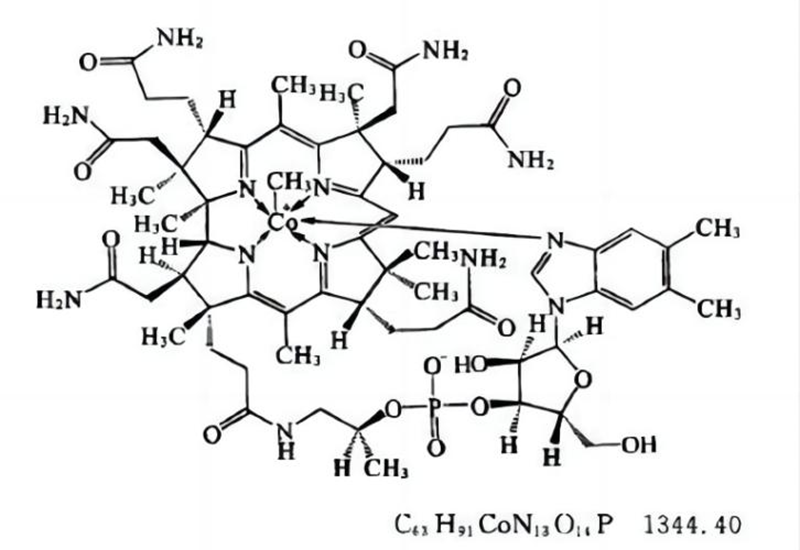
Introduction of Vitamin B12 Series Products
Vitamin B12 is a general term for vitamin B group chemicals with a cobalt ring structure. There are four types of vitamin B12 family: cyanocobalamin, hydroxocobalamin, adenosylcobalamin and methylcobalamin, but clinically used vitamin B12 usually refers to cyanocobalamin.
Cyanocobalamin and hydroxocobalamin have no direct biological activity. Cyanocobalamin is a prodrug, which can be converted into methylcobalamin and adenosylcobalamin in the human body. Methylcobalamin and adenosylcobalamin are the two active coenzyme forms of vitamin B12 in the human body.
Cyanocobalamin and hydroxocobalamin are dark red crystals or crystalline powder; adenosylcobalamin is yellow-orange hexagonal crystals, which turn dark red when exposed to air; methylcobalamin is bright red needle-like crystals or crystalline powder.
All four injections of cobalamin are red. In the storage of ordinary medicines, it is necessary to keep them away from sunlight. Cyanocobalamin is the most stable one, and generally it will not be degraded by sunlight; adenosylcobalamin and methylcobalamin are unstable when exposed to sunlight, and must be strictly protected from sunlight, and the injection time must also be shortened.
The four cobalamins can prevent and treat red blood cell anemia and treat peripheral neuropathy. In the human body, we can only use adenosylcobalamin and methylcobalamin directly, cyanocobalamin and hydroxocobalamin need to be converted into adenosylcobalamin and methylcobalamin by the organelles in the liver before they can be utilized by the human body. For people with liver diseases, such as hepatitis and cirrhosis, adenosylcobalamin and methylcobalamin should be directly supplemented to reduce the burden on the liver, and patients with liver function impairment can be given priority.
Physical & Chemical Properties of Mecobalamin
| Melting Point | >190℃(dec.) |
| Solubility | Slightly soluble in DMSO and water, sparingly soluble in Methanol |
| Acid Coefficient | Pk1:7.64(+1) (25℃) |
| Stability | Light sensitive |
| Form | Solid |
| Color | Dark Red |
Application of Mecobalamin
It is used to treat nervous system diseases, relieve pain and numbness, quickly relieve neuralgia, improve pain caused by cervical spondylosis, and treat sudden deafness, etc.
Specifications of Mecobalamin
| Test Items | Specifications | Test Methods |
| Appearance | Dark red crystals or crystalline powder | JP MonographVisual method |
|
Identification |
(1) UV: Compare the spectrum with the reference spectrum, both spectra exhibit similar intensities of absorption at the same wavelengths. | JP Monograph/JP <2.24> |
| (2) Cobalt: Meets JP requirement | JP Monograph | |
| Clarity and color of solution | The solution is clear and red color | JP Monograph |
|
Related substances |
Each area of the peaks other than mecobalamin is not more than 0.5% of the peak area of mecobalamin | JP Monograph/JP <2.01> |
| The total area of the peaks other than mecobalamin is not more than 2.0% | JP Monograph/JP <2.01> | |
| Water | ≤11.5% | JP Monograph/JP <2.48> |
| Assay(on the anhydrous basis) | 98.5%-101.0% | JP Monograph |
| Acetone | ≤5000ppm | In house/(GC) |
| The total aerobic microbial count | ≤1000cfu/g | ChP 2020 <1105> |
| The total combined yeasts/mould count | ≤100cfu/g | ChP 2020 <1105> |
Packaging
100g/tin or 1kg/tin, the outer package is carton box.
Storage Conditions
Preserved in unopened containers in a cool dry place before using; kept away from direct sunlight, heat and moisture.
Shelf Life
36 months if stored under above conditions.