Folic Acid
Brief Introduction:
Folic acid is a water-soluble vitamin, also known as vitamin B9, and is a B vitamin. Folic acid is a derivative of pteridine, it was originally isolated from the liver, later, it was found that the green leaves of plants (such as spinach leaves) are very rich in folic acid. Human intestinal bacteria can also synthesize folic acid, so it is generally not easy to be deficient.
When the human body has poor absorption and metabolic disorders, or long-term use of intestinal probiotics, folic acid deficiency may occur. Folic acid is widely found in pears, broad beans, beets, spinach, cauliflower, celery, citrus, nuts and soy foods. It is also rich in some animal foods, including offal, eggs, fish, etc.
Pregnant women should take more than 350 micrograms of folic acid per day. When the daily intake of folic acid by the human body is maintained at 3.1 micrograms per kilogram per day, the body can have an appropriate amount of folic acid reserves.
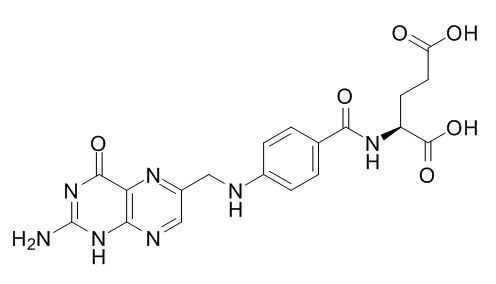
Applications:
|
Usage limit: |
1) GB 14880-94: formula food for infants and young children 380-700 μg/kg; special food for pregnant women and lactating women 2000-4000 μg/kg. 2) GB 2760-2002: 0.002-0.0075g/kg for food for pregnant women and breast milk; 0.6-1.35mg/kg for solid drinks; 1000-3000μg/kg for non-washed rice and flour; 740μg/100g for milk powder for pregnant women and nursing mothers (label The usage amount should be marked as 54g/d); milk-containing solid beverages 0.23-0.38mg/100g; instant breakfast cereals 1000-2500μg/kg; jelly 50-100μg/kg; cocoa powder and other flavored nutritional solid drinks, 3000- 6000μg/kg (the corresponding nutritional milk drink reduces the dosage according to the dilution factor). 3) FDA §172.345, 2000 (daily): 0.1mg for infants; 0.3mg for children under 4 years old; 0.4mg for over 4 years old; 0.8mg for pregnant and lactating women. | ||
|
Standards for maximum allowable use of food additives and maximum allowable residues: |
The Chinese name of the food that allows the use of this additive | Additive Function | Maximum Allowed Usage(g/kg) |
| Sports nutrition food |
Nutrition Supplements |
60 ~ 400μg | |
|
Solid drink |
157~313μg/kg (based on the diluted liquid beverage, the amount of solid beverages should be increased according to the dilution factor) | ||
| Follow-up infant and toddler formula | 0.03 ~ 0.3mg/100g | ||
| Biscuit | 39 ~ 78μg/100g | ||
|
Uses: |
1) Biochemical research; clinical drugs are vitamin B family, used for the treatment of pregnancy and infant giant cell anemia. | ||
| 2) Anti-anemia drugs for symptomatic or nutritional giant cell anemia. | |||
| 3) Used as a biochemical reagent, also used in the pharmaceutical industry, etc. | |||
| 4) Folic acid is an anti-anemia drug. When livestock and poultry lack folic acid, their appetite will decrease, their growth will be hindered, and their feathers will grow poorly. Dosage 0.5-1.0mg/kg. | |||
| 5) As a food fortifier. It can be used in food for infants and young children, and the dosage is 380-700 μg/mg; it can be used in special foods for pregnant women and nursing mothers at 2-4 mg/kg. | |||
| 6) Anti-anemia drug; also prevents most neural tube defects (NTDs). | |||
| 7) Used in the polyamide industry to prepare nylon and also as a raw material for saturated polyurethane | |||
| 8) As a feed additive, folic acid is widely used in livestock and poultry such as pigs, dairy cows and chickens. | |||
Specifications of our Food Grade Folic Acid:
| Testing Items | Specifications |
| Appearance | Yellowish or orange crystalline powder |
| Identification | Ratio: A256/A365: 2.80 ~ 3.00 |
| Water | Not more than 8.5% |
| Residue on Ignition | Not more than 0.3% |
| Cadmium(Cd) | Not more than 1mg/kg |
| Mercury(Hg) | Not more than 1mg/kg |
| Arsenic(As) | Not more than 3mg/kg |
| Lead(Pb) | Not more than 2mg/kg |
| Total Aerobic Plate Count | Not more than 1000CFU/g |
| Yeasts & Moulds | Not more than 100CFU/g |
| Coliforms | Not more than 3.0MPN/g |
| Salmonella | Negative |
| Assay HPLC(On the Anhydrous Basis) | 96.0% ~ 102.0% |
Specifications of our Pharmaceutical Grade Folic Acid:
| Testing Items | Specifications |
| Appearance | Yellowish or orange crystalline powder |
| Identification | Ratio: A256/A365: 2.80 ~ 3.00 |
| Organic Volatile Impurities | Meets the requirements |
| Related Compounds | Not more than 2.0% |
| Residue on Ignition | Not more than 0.3% |
| Water | Not more than 8.5% |
| Assay HPLC(On the Anhydrous Basis) | 97.0% ~ 102.0% |
Specifications of our Feed Grade Folic Acid:
| Testing Items | Specifications |
| Appearance | Yellow to orange yellow crystalline powder |
| Identification | Ratio: A256/A365: 2.80 ~ 3.00 |
| Organic Volatile Impurities | Meets the requirements |
| Residue on Ignition | Not more than 0.3% |
| Water | Not more than 8.5% |
| Assay HPLC (On the Anhydrous Basis) | 95.0% ~ 102.0% |
Packaging of our Folic Acid:
1kg/Aluminum Foil Bag, 5kg/Carton, 10kg/Carton, 25kg/Carton or 25kg/Fibre Drum.
Storage Conditions:
Preserved in unopened original containers in a cool dry place before using; kept away from sunlight, heat and moisture.
Shelf Life:
36 months under above mentioned conditions.













