Dexmedetomidine
Brief Introduction:
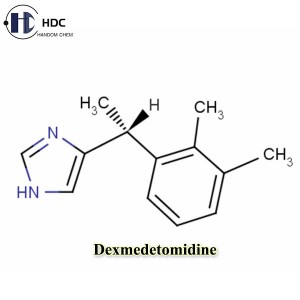
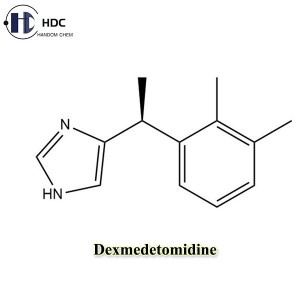
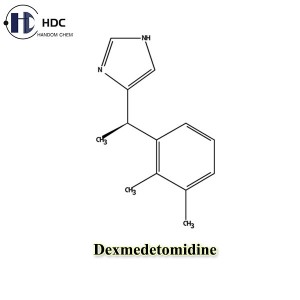
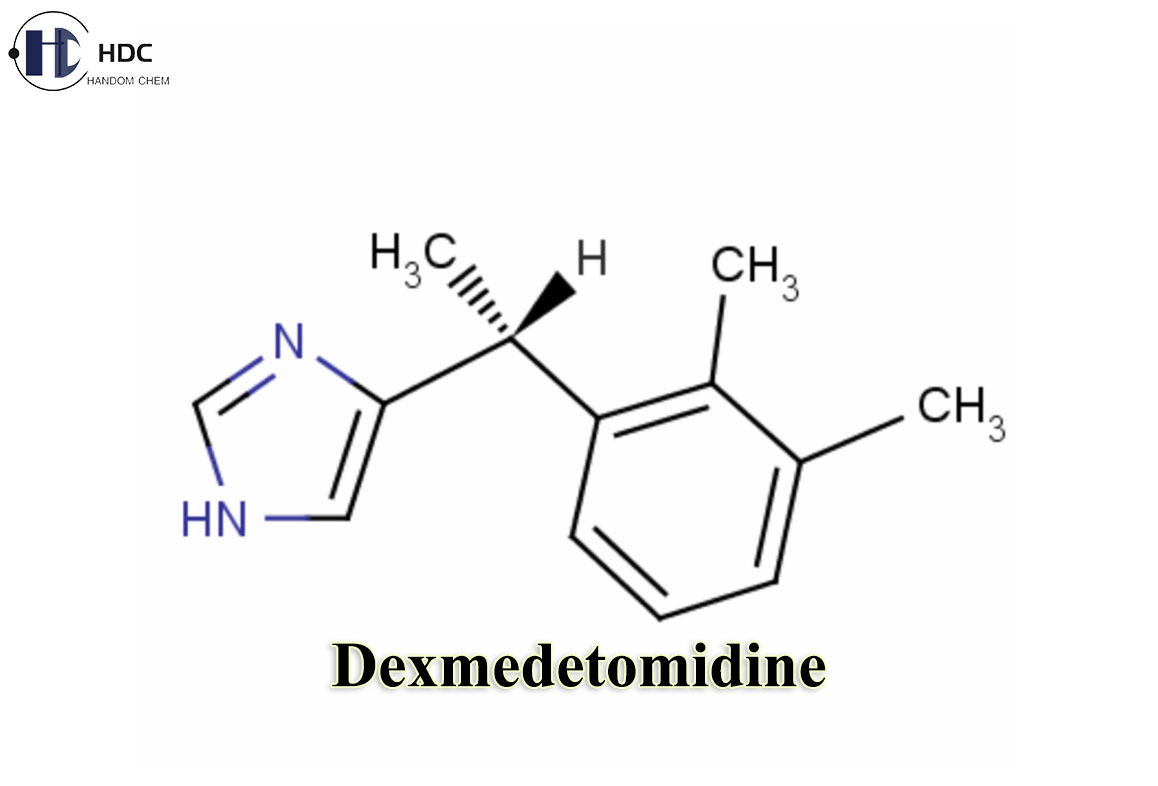
Dexmedetomidine is the dextrorotatory isomer of medetomidine and is a highly selective α2-adrenergic receptor agonist. Unlike medetomidine hydrochloride for veterinary use, dexmedetomidine is mainly used in human medicine, especially in the field of intensive care unit (ICU) and anesthesia.
Mechanism of Action:
Selectively activates α2-adrenergic receptors in the central and peripheral nerves, inhibits sympathetic nerve activity, and produces:
- ◎ Deep Sedation: Similar to natural sleep, patients are easily awakened.
- ◎ Analgesia: Reduces pain signal transmission.
- ◎ Anti-anxiety: Reduces stress response.
- ◎ Stabilizes Hemodynamics: Reduces cardiovascular fluctuations during surgery or ICU.
Main Uses:
▲ ICU Sedation: Used for critically ill patients who need mechanical ventilation (such as postoperative, severe respiratory failure).
▲ Anesthetic Assistance: Preoperative sedation, intraoperative reduction of anesthetic dosage, postoperative analgesia.
▲ Short-term Procedural Sedation: Such as endotracheal intubation, endoscopic examination, etc.
▲ Children's Sedation: Used for pediatric imaging examinations in some cases.
Specifications of our Dexmedetomidine:
| Test Items | Specifications |
| Appearance | Off-white to white powder |
| Melting Point | 145℃ ~ 152℃ |
| Specific Rotation | +72.0°~+76.0° |
| Related Substances | Not more than 1.0% |
| Levmedetomidine | Not more than 1.0% |
| Loss on Drying | Not more than 1.0% |
| Residue on Ignition | Not more than 0.1% |
| Heavy Metals | Not more than 10ppm |
| Assay | Not less than 99.0% |
Features and Advantages:
★ High Controllability:
The sedation depth is easy to adjust, and the patient can follow the instructions.
★ Mild Respiratory Depression:
Less impact on breathing compared to benzodiazepines (such as Midazolam).
★ No Significant Addiction:
Suitable for long-term ICU sedation.
★ Reversibility:
α2 receptor antagonists (such as Atipamezole) can be used to antagonize its effects.
Adverse Reactions:
※ Common: hypotension, bradycardia (especially at loading doses).
※ Other: dry mouth, transient hypertension (during initial dosing), nausea.
※ Rare: respiratory depression (at high doses or in combination with other sedatives).
※ Precautions:
! Contraindications: severe heart block, hypotension, uncontrolled hypovolemia.
! Dosage Control: needs to be adjusted according to body weight and condition, and intravenous infusion needs to be strictly monitored.
! Special Populations: pregnant women, lactating women, and the elderly should use with caution.
! Drug Interactions: be cautious when used in combination with anesthetics, antihypertensive drugs, and beta-blockers.
Difference from Medetomidine:
☝ Structure: Medetomidine is a racemic isomer (including levorotatory and dextrorotatory isomers), while dexmedetomidine is a single active isomer, which is more potent and more selective.
☝ Use: Medetomidine is mainly used in veterinary medicine, while dexmedetomidine is used exclusively in humans.
☝ Safety: Dexmedetomidine has undergone rigorous clinical trials, and its indications and side effects management are more clearly defined.
Drug Forms:
Injection: requires intravenous infusion, the concentration is usually 100 μg/mL, and is used after dilution.
♣ Dosage Method: Loading Dose + Maintenance Infusion, which is adjusted by the doctor according to the condition.
Packaging:
10g/Bag, 20g/Bag, 50g/Bag, 100g/Bag, 500g/Bag, 1kg/Bag or according to the specific requirements from customers.
Storage Conditions:
Preserved in unopened original containers in a cool dry place before using; kept away from direct sunlight, heat and moisture.
Shelf Life:
24 months from the date of manufacturing when stored under the above conditions.